What Is The Meaning Of Ah In Battery
So, picture this: I’m on this epic road trip, right? Miles and miles of open highway, music blasting, windows down. Pure bliss. Then, all of a sudden, my phone decides it’s had enough. The dreaded low battery warning flashes, and then… black screen. Ugh. That feeling of being completely disconnected, unable to navigate, take a photo, or even pretend I’m busy, is just the worst. It got me thinking, though. We all rely on these little powerhouses, but do we really understand what makes them tick? Especially when we see those mysterious letters and numbers like ‘Ah’ plastered all over them.
Let’s be honest, most of us just grab a charger when the red line appears and don’t give it another thought. But that ‘Ah’ thing? It’s kind of a big deal. It’s like the secret handshake of battery life, the unspoken promise of how long your device should last. And, like many things in life, it’s not always as straightforward as it seems. So, pull up a digital chair, and let’s unravel the mystery of ‘Ah’ in the wonderful, sometimes frustrating, world of batteries. Consider this your friendly, no-judgment-zone deep dive.
The ‘Ah’ Factor: It’s Not Just About How Much Juice Is Left
Okay, so ‘Ah’ stands for Ampere-hour. Easy enough, right? Well, kind of. An ampere (A) is a unit of electric current – basically, how much electricity is flowing. An hour (h) is, well, an hour. So, Ampere-hour is the rate at which a battery can deliver electricity over a specific period. Think of it like this: if you have a battery with 10Ah, it could theoretically supply 10 Amperes for 1 hour, or 5 Amperes for 2 hours, or even 1 Ampere for 10 hours.
This is where things start to get a little more nuanced. It’s not just a hard and fast number. The Ah rating is a theoretical capacity under ideal conditions. And, spoiler alert, we rarely operate in ideal conditions, do we? Life, and our electronics, are messy. But it’s the best benchmark we’ve got. It’s the battery manufacturer’s way of saying, “Hey, this is what you can expect, generally speaking.”
So, when you’re looking at a power bank, a car battery, or even the tiny battery in your smartwatch, that ‘Ah’ number is your first clue about its potential longevity. A bigger ‘Ah’ number generally means a longer runtime. Simple enough, but as we’ll see, there are more layers to this electrical onion.
Why Does ‘Ah’ Matter So Much? (Besides Avoiding That Black Screen of Doom)
Imagine you’re planning a camping trip. You need to know how much food and water to pack, right? You wouldn’t just guess. You’d estimate based on how many people are going and how long you’ll be gone. The ‘Ah’ rating is the battery equivalent of that planning. It helps you understand:
- Runtime Expectations: How long can your device realistically operate on a single charge? This is the most direct benefit. If you’re a heavy user, you’ll want a higher ‘Ah’ battery. If you’re a light user, a smaller one might suffice.
- Compatibility: Sometimes, especially with DIY projects or replacing components, understanding the ‘Ah’ is crucial for ensuring you’re using a battery that’s appropriately sized for the power demands of the device. Too small, and it won’t last. Too big, and you might have other issues (though usually, it’s the other way around).
- Performance Comparisons: When you’re comparing different batteries, the ‘Ah’ rating is your primary metric. It allows you to see which one offers more stored energy.
It’s like going to the grocery store. You see a gallon of milk and a pint of milk. The gallon is clearly going to last longer. The ‘Ah’ is the battery’s ‘gallon size’. It’s the fundamental measure of how much ‘stuff’ (electrical charge) it can hold.

The Nuances: Not All Ah Is Created Equal
Alright, so we’ve established that ‘Ah’ is important. But here’s where things get a little more interesting, and maybe a touch ironic. That ‘Ah’ rating? It’s usually specified at a particular discharge rate and temperature. And guess what? Those conditions are often laboratory-perfect. Sigh. Life isn’t a lab, is it?
One of the biggest factors that affects a battery’s usable capacity is the discharge rate. This is how quickly you're drawing power from the battery. If you’re using a device that draws a lot of current (think high-performance gaming on your phone, or starting a car engine), the battery’s effective ‘Ah’ will be lower than its advertised rating. It’s like trying to drink a milkshake through a tiny straw versus a wide one. You get less through the straw per second, even if the milkshake volume is the same.
This is a concept known as the Peukert’s Law (don’t worry, you don’t need to remember the name, but it’s a real thing!). Essentially, the faster you discharge a battery, the less total energy you can get out of it. So, that 10Ah battery might only give you 8Ah if you’re really hammering it.
Temperature is another sneaky saboteur. Batteries perform best at moderate temperatures. If it’s freezing cold, the chemical reactions inside slow down, and you’ll get less usable capacity. If it’s blazing hot, it can degrade the battery over time, and while it might perform okay in the short term, it’s not good for its long-term health. Ever notice how your phone battery drains faster in winter? Yep, temperature is a major culprit.
So, while ‘Ah’ gives you a good starting point, remember it’s a theoretical maximum. Your actual experience might vary depending on how you use your device and the environmental conditions. It's like buying a car with a stated MPG – your real-world MPG will depend on your driving style, traffic, and the road conditions, right?

Decoding the Labels: What You're Actually Seeing
You’ll often see ‘Ah’ paired with a voltage rating (V). For example, a battery might be rated at 12V, 50Ah. This is important because power (measured in Watts) is a combination of voltage and current. Power (W) = Voltage (V) x Current (A). So, a 12V, 50Ah battery can deliver 12V at 5A for 10 hours (50Ah / 10h = 5A), or 12V at 10A for 5 hours (50Ah / 5h = 10A), and so on.
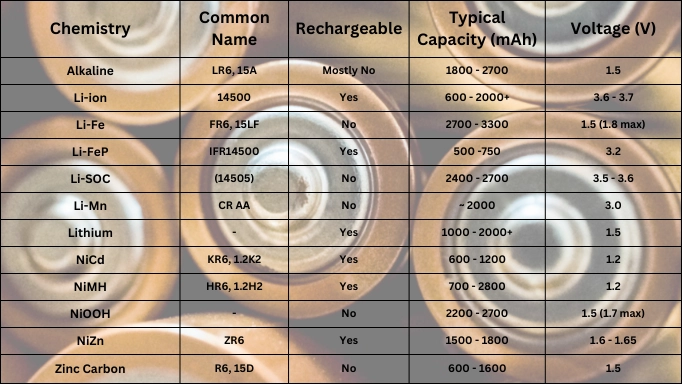
Sometimes, especially with smaller batteries like those in smartphones or laptops, you’ll see the capacity listed in milliampere-hours (mAh). This is just a smaller unit: 1 Ah = 1000 mAh. So, a 3000 mAh battery is the same as a 3 Ah battery. They just use ‘milli’ when the numbers get smaller to avoid writing too many zeros. Convenient, right? It’s like the difference between saying ‘one thousand meters’ and ‘one kilometer’. Same distance, just a different way of expressing it.
And then there are lithium-ion batteries, which are everywhere. You might see a Watt-hour (Wh) rating instead of or in addition to Ah. This is often considered a more accurate measure of energy because it accounts for voltage. Since the voltage of a lithium-ion battery can vary during its discharge cycle, Wh gives a more stable picture of the total energy stored. You can calculate Wh by multiplying the Ah rating by the battery’s nominal voltage. So, a 50Wh battery with a 12V nominal voltage would be approximately 4.17Ah (50Wh / 12V ≈ 4.17Ah). This is useful when comparing batteries with different voltage chemistries.
The Battery's Life Cycle: Beyond Just ‘Ah’
It’s not just about the initial ‘Ah’ rating. Batteries degrade over time. This is called cycle life. Every time you charge and discharge a battery, it loses a tiny bit of its capacity. Think of it like running laps. You can run a lot of laps, but eventually, you’ll get tired. Batteries are similar; they have a finite number of charge cycles they can endure before their maximum capacity significantly drops.
This means that a brand-new battery with a certain ‘Ah’ rating will perform better than the same battery after a year of regular use. The ‘Ah’ rating of an older battery is effectively lower than its original specification. Manufacturers often rate batteries for a certain number of charge cycles (e.g., 500 cycles, 1000 cycles) before the capacity drops to, say, 80% of its original value.
So, when you’re looking at a device or a battery, the ‘Ah’ is a snapshot of its potential at that moment. But the health and age of the battery also play a huge role in how long it will actually last. This is why that older laptop or phone might seem to die so much faster, even if it has a battery with the same theoretical ‘Ah’ rating as a newer one.
It's a bit like comparing a brand-new car with a well-maintained, but older, car. Both might have the same engine size on paper, but the newer one will likely perform better and last longer before needing significant repairs. The ‘Ah’ is the engine size, but the cycle life and health are like the mileage and maintenance history.
Practical Implications: Choosing the Right Battery for You
So, what does all this mean for you, the everyday user? When you're shopping for a new gadget or a replacement battery, pay attention to the ‘Ah’ (or mAh). If you’re a power user, aim for a higher number. If you’re a casual user, a lower number might be fine and could mean a lighter or cheaper device.
Consider your usage patterns. If you’re constantly on your phone playing games or watching videos, you’ll drain a battery much faster than someone who just uses it for calls and texts. In this case, a higher ‘Ah’ battery is a must. A portable power bank with a high ‘Ah’ rating is your best friend if you’re frequently away from a power outlet.
For larger applications, like solar power systems or electric vehicles, understanding ‘Ah’ and how it relates to voltage and power demands becomes even more critical. You need to ensure your battery bank can provide enough Amperes for the required time without excessive voltage sag or premature degradation. It’s all about matching the battery’s capacity to the load it needs to serve.

And don’t forget about battery maintenance! While you can’t directly control the chemical degradation, following manufacturer recommendations for charging and storage can help maximize the lifespan of your battery. Avoiding extreme temperatures and not constantly keeping your battery at 100% or 0% charge can also help preserve its health. It’s like taking care of your health – small, consistent habits make a big difference in the long run.
The Future of ‘Ah’ (And Batteries in General)
The quest for better batteries is ongoing. Scientists are constantly developing new battery chemistries and designs that offer higher energy density (more ‘Ah’ in the same size), faster charging, and longer cycle lives. We're seeing advancements in solid-state batteries, lithium-sulfur batteries, and more, all aiming to overcome the limitations of current lithium-ion technology.
As battery technology evolves, the way we measure and understand capacity might also change. But for now, ‘Ah’ remains the fundamental metric. It’s the common language we use to talk about how much stored energy a battery holds. It’s the yardstick by which we measure potential longevity.
So, the next time you see that ‘Ah’ on a battery, you’ll know it’s more than just a random number. It’s a crucial piece of information that helps you understand the power you’re holding in your hands. It’s the promise of staying connected, of powering your adventures, and of avoiding that dreaded black screen of disconnection. And in today’s world, that’s a pretty big deal, wouldn’t you agree?
It’s a surprisingly complex topic hidden behind a simple two-letter abbreviation. But understanding it a little better means making more informed choices, getting the most out of your devices, and maybe, just maybe, feeling a tiny bit more in control of the technology that powers our lives. Now go forth and conquer your battery-related queries with newfound knowledge!
