Monetary Policy: Definition, Tools, And Goals

Hey there, money-curious friend! Ever heard the term "Monetary Policy" and felt your eyes glaze over a little? Maybe you pictured stern-looking folks in suits discussing graphs that looked like abstract art? Well, put those thoughts aside! We're about to demystify it all, and I promise, it's way less intimidating than it sounds.
Think of it less like a stuffy economics lecture and more like a chat over coffee (or your beverage of choice). We're going to dive into what monetary policy is, the cool gadgets and levers that central banks use, and what they're actually trying to achieve with all their financial wizardry. Spoiler alert: it affects your wallet, your job, and pretty much everything in between!
So, buckle up! Or, you know, just lean back comfortably. This isn't rocket science, just the art of managing an economy without everyone running around screaming, "Where did all my money go?!" or "Why is a loaf of bread costing me an arm and a leg?!"
Monetary Policy: What Even Is It?
Alright, let’s kick things off with the big question. What is monetary policy? At its heart, it’s basically the fancy term for how a country’s central bank (like the Federal Reserve in the US, the European Central Bank, or the Bank of England) manages the supply of money and credit in the economy.
Imagine your country’s economy is a giant car. The central bank? It’s the driver, and monetary policy is how they adjust the gas pedal, the brake, and sometimes even the steering wheel to keep things running smoothly. Their main goal is to influence how much money is floating around and how easy (or hard) it is for people and businesses to borrow it.
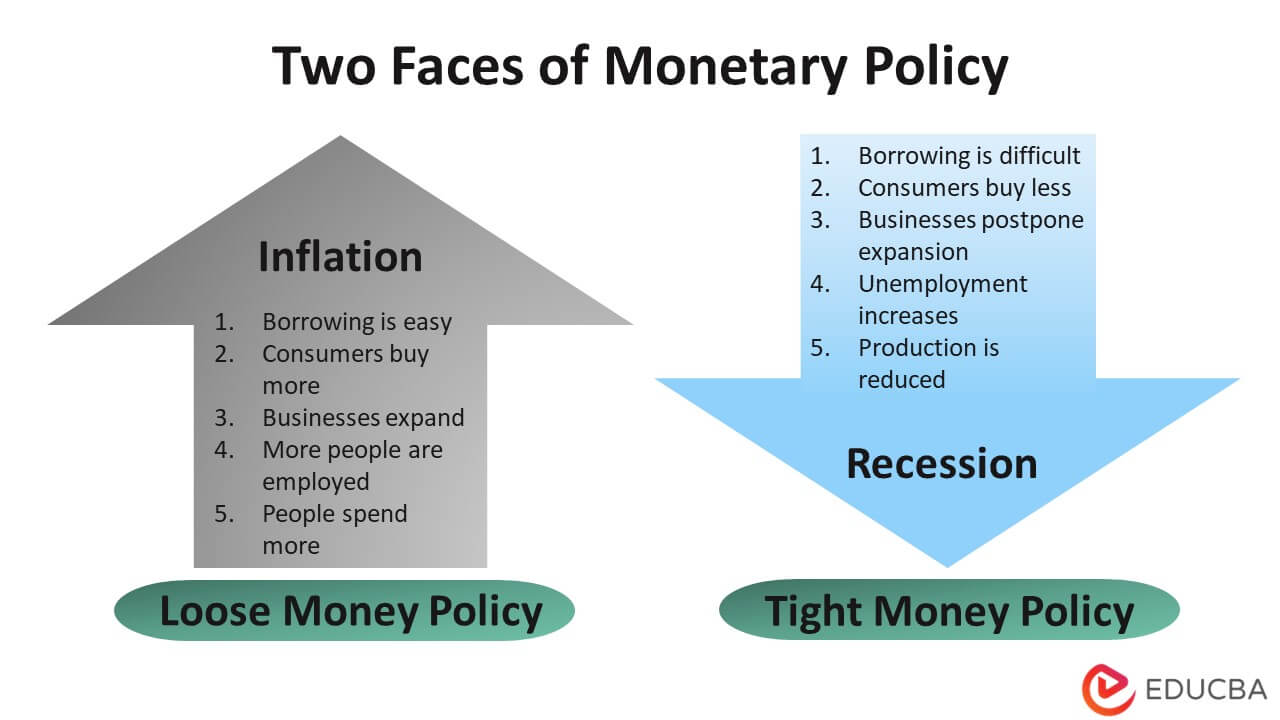
Why do they bother? Because the amount of money sloshing around, and the cost of borrowing it, has a huge impact on how well an economy performs. If there’s too much money and it’s super cheap to borrow, everyone might start spending like crazy, prices shoot up (hello, inflation!). If money is too tight and expensive, well, then businesses might struggle, people might stop buying things, and jobs could disappear (hello, recession!).
So, in essence, monetary policy is the central bank's sophisticated balancing act to keep our economic car cruising along at a nice, steady, and sustainable speed. Not too fast, not too slow. Just right, Goldilocks style!
The Central Bank's Awesome Toolbox (No Hammers, Just Clever Stuff)
Okay, so our central bank driver has a job to do. How do they actually do it? They’ve got a pretty cool set of tools in their economic toolbox. And no, they're not actual hammers and wrenches, but they get the job done!
1. Interest Rate Adjustments (The Big Knob)
This is probably the most famous tool, and often the one you hear about in the news. The central bank sets a key interest rate (sometimes called the policy rate or the discount rate, depending on the country). Think of this as the master tap on the money hose.
When the central bank raises this interest rate, it basically makes it more expensive for commercial banks (like your local bank) to borrow money from the central bank. And guess what? If it costs banks more to borrow, they’re going to charge you more to borrow! Mortgages get pricier, car loans become more expensive, business loans too. This usually slows down spending and investing, cooling off the economy if it's getting too hot.
Conversely, when the central bank lowers the interest rate, it's like opening the tap wider. It becomes cheaper for banks to borrow, so they can lend money to you and me at lower rates. Suddenly, that new car, house, or business expansion looks a lot more affordable. This encourages spending and investment, giving the economy a little boost if it's feeling sluggish.
It's all about making borrowing more or less appealing. Pretty clever, right?
2. Open Market Operations (The Sneaky Handshake)
This sounds super technical, but it’s actually quite straightforward when you break it down. Open Market Operations (OMOs) involve the central bank buying or selling government bonds (which are essentially IOUs from the government) in the open market.
When the central bank wants to increase the money supply (inject more cash into the economy), it buys government bonds from commercial banks. It pays the banks with new money, which then sits in the banks’ reserves, ready to be lent out. Ta-da! More money flowing around, often leading to lower interest rates.
If the central bank wants to decrease the money supply (suck some cash out of the economy), it sells government bonds to commercial banks. The banks pay the central bank with money they would otherwise lend out, reducing their reserves. Less money available to lend, often pushing interest rates up. It’s like a financial game of peek-a-boo with money!
3. Reserve Requirements (The Bank's Piggy Bank Rules)
This tool dictates how much cash commercial banks must keep in reserve and not lend out, usually as a percentage of their deposits. Think of it as the minimum amount a bank has to keep in its "piggy bank" at all times.
If the central bank raises the reserve requirement, banks have less money available to lend. This tightens the money supply and can increase interest rates. It's like telling a bank, "Hey, you need to save more of your allowance, less spending for you!"
If they lower the reserve requirement, banks suddenly have more money to lend out, which increases the money supply and can lower interest rates. "Go on, spend some of that allowance, you've earned it!"
This tool isn't used as frequently as interest rate adjustments or OMOs because it can have a pretty dramatic and sudden impact on the banking system. It’s more of a blunt instrument, usually reserved for bigger shifts.
4. Quantitative Easing/Tightening (QE/QT - The Bigger Hammer)
Okay, these are the heavy hitters, often brought out during big economic crises or when traditional tools aren't quite cutting it. Quantitative Easing (QE) is when the central bank buys a massive amount of long-term government bonds or other assets from banks and other financial institutions. It's OMOs on steroids!
The goal? To pump huge amounts of money directly into the financial system, push down long-term interest rates (like for mortgages), and encourage lending and investment when the economy is really struggling, often even when short-term interest rates are already near zero. It’s like trying to jump-start a car that’s completely dead by giving it a massive charge.
Quantitative Tightening (QT) is the reverse: the central bank stops reinvesting the money from maturing bonds or even actively sells them. This effectively shrinks the money supply and pulls cash out of the system. It's like slowly disconnecting that massive charge once the car is running well again.
These are definitely the "break glass in case of emergency" tools, used when the economic seas are exceptionally choppy.
.png)
The Master Plan: What Are They Trying to Achieve? (The Goals!)
So, the central bank has all these powerful tools. But what's the grand vision? What are they actually trying to achieve by fiddling with interest rates and buying bonds? They have a few core goals, which are super important for all of us.
1. Price Stability (Keeping Things Predictable)
This is arguably the central bank's most important mission. Price stability means keeping inflation (the general increase in prices over time) low and predictable. Think of it as keeping the cost of your groceries, gas, and rent from going absolutely bonkers.
A little bit of inflation is actually considered healthy for an economy, as it encourages spending and investment (because your money will be worth slightly less tomorrow, so you might as well spend it today!). But too much inflation (hyperinflation, anyone?) makes your money lose value super fast, eroding your savings and making it impossible for businesses to plan. And too little inflation (or even deflation, where prices fall) can also be bad, as people might delay purchases hoping prices will drop further, stalling economic activity. It’s all about hitting that sweet spot!
So, the central bank aims for a steady, manageable rate of inflation – typically around 2% in many developed economies. It’s like setting the thermostat in your house: not too hot, not too cold, just comfortable!
2. Maximum Sustainable Employment (Jobs, Jobs, Jobs!)
Another crucial goal is to foster maximum sustainable employment. This means getting as many people working as possible without causing the economy to overheat and trigger too much inflation. It's about ensuring that everyone who wants a job can find one, and that businesses have access to the workforce they need.
When the economy is strong and growing, businesses hire more people. By keeping interest rates low and money flowing, the central bank can encourage this growth. However, if the economy gets too hot and there are more jobs than people, wages can start to climb rapidly, contributing to inflation. It's a delicate balance, like finding the perfect speed limit on the economic highway.
3. Moderate Long-Term Interest Rates (Stable Borrowing)
This goal is a bit more subtle but incredibly important for long-term planning. The central bank aims for moderate long-term interest rates. This means keeping the cost of borrowing for things like mortgages, car loans, and business investments stable and at reasonable levels over time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/expansionary-monetary-policy-definition-purpose-tools-602173d0ef8a44bda1584fc15ba020e2.jpg)
Why is this a big deal? Because stability allows businesses to invest in new projects with confidence, knowing their borrowing costs won’t suddenly skyrocket. It also makes it easier for families to plan for big purchases like homes. Think of it as providing a predictable financial landscape, rather than a wild rollercoaster ride, so everyone can plan for their future with a bit more certainty.
4. Financial Stability (Keeping the System From Crashing)
Finally, and perhaps most importantly (especially after some recent financial crises!), central banks are deeply committed to ensuring financial stability. This means preventing severe disruptions or crashes in the banking and financial system that could have catastrophic effects on the broader economy.
They do this by supervising banks, making sure they’re not taking on too much risk, and acting as a "lender of last resort" to inject liquidity into the system if banks suddenly find themselves short on cash. It’s like having a superhero safety net for the entire financial system, making sure that if one part stumbles, the whole thing doesn't come tumbling down.
Bringing It All Together: Your Role in the Big Picture!
So, there you have it! Monetary policy isn't just for economists in ivory towers. It's the central bank's way of trying to keep our economic boat sailing smoothly, using a range of tools to hit some really important goals. From controlling inflation to fostering job growth and keeping the financial system steady, their decisions ripple through almost every aspect of our lives.
The next time you hear about interest rates changing or the central bank making a big announcement, you'll know exactly what they're up to and why it matters. You're no longer just a passenger; you've got a roadmap to understanding the economic journey!
It's pretty amazing, isn't it? Knowing that there are dedicated folks working behind the scenes, pulling levers and turning knobs (metaphorically speaking, of course!) to keep our economic world humming along. And now, you're in the know!
So, go forth, my newly enlightened friend! Maybe share your newfound wisdom at your next gathering. Just try not to get too deep into quantitative tightening over appetizers, unless you really want to clear the room. But seriously, understanding these big concepts empowers you to make smarter financial decisions and engage more meaningfully with the world around you. And that, my friend, is something to smile about!
